Sisak S, Banin E, Blumenthal EZ.
Med Hypotheses. 2004;62(5):808-16.
Department of Ophthalmology, Brasov County Hospital, Brasov, Romania.
ABSTRACT:
PURPOSE: In this article we question a basic concept in retinal pathology, which views the retina as composed primarily of neural elements, in a single compartment.
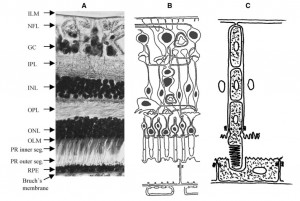
METHODS: We suggest an alternative approach, centering on the epithelial-glial elements of the retina, dividing the retina into two distinct compartments. The framework of these two compartments is composed of two epithelial-like monostratified cell layers facing each other by their apical surfaces. This model is in agreement with the embryological development of the retina.
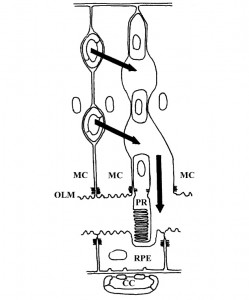
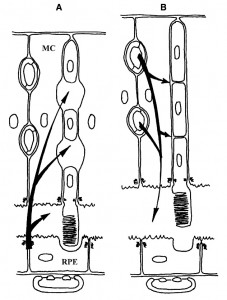
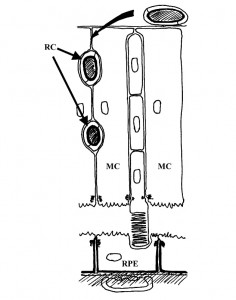
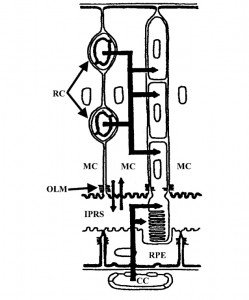
RESULTS: Each compartment is composed of a monostratified cell layer in which neural elements are embedded and each is supplied by a different blood supply. The inner compartment, also referred to as the Muller cell compartment, extends between the inner and outer limiting membranes. The outer, or RPE, compartment extends between the outer limiting and Bruch’s membranes. The border between the two compartments is formed by the outer limiting membrane (OLM). One simplified example utilizing the two-compartment concept is as follows: inner compartment edema (inner blood-retinal barrier breakdown) may manifest as cystoid edema, but not as serous retinal detachment, while outer compartment edema (outer blood-retinal barrier breakdown) may manifest as serous retinal detachment but not as cystoid edema, as long as the integrity of the OLM is maintained.
CONCLUSION: A two-compartment approach to the structure of the retina, centering on non-neural elements, may enhance our understanding of some retinal pathologies. Various retinal diseases, mainly of vascular origin, are limited to one of the two compartments.
Figures from this article: