Sample PA, Chan K, Boden C, Lee TW, Blumenthal EZ, Weinreb RN, Bernd A, Pascual J, Hao J, Sejnowski T, Goldbaum MH.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004 Aug;45(8):2596-605.
Hamilton Glaucoma Center, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California-San Diego, La Jolla, 92093-0946, USA. psample@eyecenter.ucsd.edu
ABSTRACT:
PURPOSE: To determine whether an unsupervised machine learning classifier can identify patterns of visual field loss in standard visual fields consistent with typical patterns learned by decades of human experience.
METHODS: Standard perimetry thresholds for 52 locations plus age from one eye of each of 156 patients with glaucomatous optic neuropathy (GON) and 189 eyes of healthy subjects were clustered with an unsupervised machine classifier, variational Bayesian mixture of factor analysis (vbMFA).
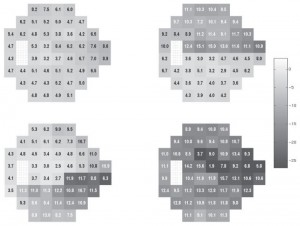
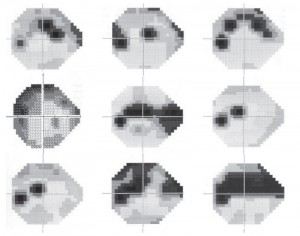
RESULTS: The vbMFA formed five distinct clusters. Cluster 5 held 186 of 189 fields from normal eyes plus 46 from eyes with GON. These fields were then judged within normal limits by several traditional methods. Each of the other four clusters could be described by the pattern of loss found within it. Cluster 1 (71 GON + 3 normal optic discs) included early, localized defects. A purely diffuse component was rare. Cluster 2 (26 GON) exhibited primarily deep superior hemifield defects, and cluster 3 (10 GON) held deep inferior hemifield defects only or in combination with lesser superior field defects. Cluster 4 (6 GON) showed deep defects in both hemifields. In other words, visual fields within a given cluster had similar patterns of loss that differed from the predominant pattern found in other clusters. The classifier separated the data based solely on the patterns of loss within the fields, without being guided by the diagnosis, placing 98.4% of the healthy eyes within the same cluster and spreading 70.5% of the eyes with GON across the other four clusters, in good agreement with a glaucoma expert and pattern standard deviation.
CONCLUSIONS: Without training-based diagnosis (unsupervised learning), the vbMFA identified four important patterns of field loss in eyes with GON in a manner consistent with years of clinical experience.
Figures from this article: